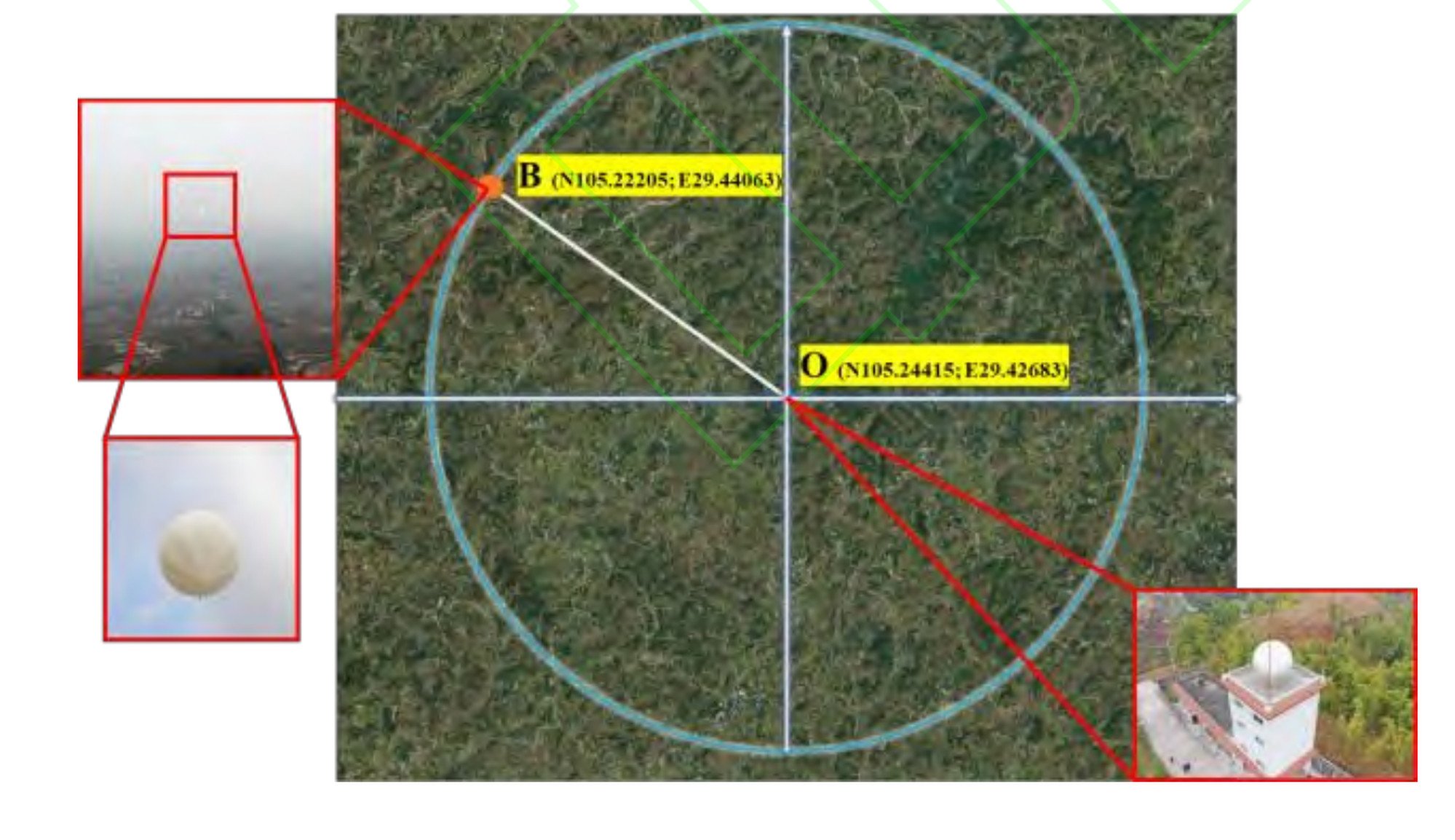
Chinese scientists may have achieved a significant breakthrough in aerial surveillance by upgrading ordinary weather radars to detect even the smallest airborne objects. This innovative radar technology allows the detection of tiny high-altitude balloons with the same precision as spotting an F-35 stealth fighter jet, according to claims by the Hong Kong "South China Morning Post."
This advancement transforms weather radars, traditionally unable to detect such small, slow-moving objects, into highly effective surveillance tools. This capability poses potential security concerns for other nations, including the US and India.
The new technology, which only requires a software upgrade for existing weather radars, is both cost-effective and efficient. This means that China can enhance its aviation monitoring and national defense capabilities without significant investment in new hardware.
This upgrade enables weather radars to continue their primary function of weather forecasting while also monitoring small airborne objects, marking a major technological advancement. In the context of the competitive global technological landscape, this achievement underscores China's prowess in innovation.
The development is timely, considering the growing contest for aerial dominance. In early 2023, a Chinese "weather balloon" traversed the US, causing a media frenzy and embarrassing the US military, which initially failed to detect it.
Understanding the Threat: Spy Balloons
Spy balloons have a longstanding history in espionage, offering unique advantages despite the prevalence of satellites. These advanced balloons, equipped with high-tech imaging gear, can provide close-range monitoring and intercept communications. Unlike satellites, which orbit rapidly, these balloons hover at lower altitudes, capturing clearer images.
Chinese researchers have highlighted the military uses of such balloons, including creating false air situations, deploying weapons, and conducting psychological warfare and reconnaissance.
China's "Spy Balloons" in US Skies
In January 2023, a large Chinese balloon entered US airspace, initially undetected by the US military. Public pressure led to the deployment of fighter jets to track the balloon, which was eventually shot down in February 2023. Subsequent investigations revealed the balloon was transmitting navigation data back to China using an American internet service provider.
Threat to Other Countries
China's surveillance efforts extend beyond the US. Countries like Japan and India have reported mysterious aerial objects, suspected to be Chinese spy balloons. China has established its Near-Space Command, utilizing drones, robotics, and spy balloons for high-altitude surveillance under the Central Military Commission.
The Strategic Support Force (SSF), a covert unit of the People's Liberation Army (PLA), operates spy balloons and other surveillance technologies. The SSF runs tracking and command stations worldwide and has a fleet of space support ships.
The Biden administration has accused China of running a military-linked aerial surveillance program targeting over 40 countries. The US and its allies, including Japan and Taiwan, have reported multiple instances of suspected Chinese spy balloons in their airspace.
In November 2023, an unidentified flying object near Imphal airport in Manipur, India, led to the mobilization of fully loaded Rafale jets, highlighting the heightened state of alert regarding potential aerial threats from China.
Conclusion
The implications are clear: aerial surveillance has entered a new phase. While the US and other nations work to improve their detection capabilities, China has surged ahead, converting simple weather radars into advanced surveillance systems. This development signals a new era in aerial espionage, with China significantly altering the landscape of aerial security and surveillance.



:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/archetype/DUN5CIP6JVCMXF2ERRLMMXS7FM.jpg)
:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/archetype/4RAQ4T4CHNCB5E3MKQO3IF4QUE.JPG)




:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/archetype/TE25PSHSZNBH3M5JF4TB2ZC53M.png)




:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/archetype/7HGY5NE5X5BODIRG4TY4CY6DCA.jpg)

:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/archetype/W3UFL22J6NEIPPRVBYINTAGPQQ.jpg)
