Lockheed Martin, a major U.S. defense contractor, is fiercely competing for the Indian Air Force's (IAF) transport and fighter jet aircraft contracts. For the transport aircraft, Lockheed Martin is up against Airbus and Embraer.
The IAF’s transport aircraft have been crucial for Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations within India and internationally. They also play a vital role in the logistics and movement of Indian armed forces, especially in the Himalayan regions. Historically, the Ilyushin Il-76MD and Antonov An-32 aircraft have been the mainstay for almost 40 years. The recent additions of the C-17 Globemaster and C-130J-30 have extended India’s reach and payload capacity.
As India progresses towards becoming the third-largest economy, its global commitments necessitate an upgrade in the IAF’s transport capabilities. Older aircraft are nearing retirement, prompting the IAF to seek new transport aircraft with an 18 to 30-ton cargo capacity. Contenders include Embraer’s C-390, Lockheed Martin’s C-130J, and the Airbus A400M Atlas.
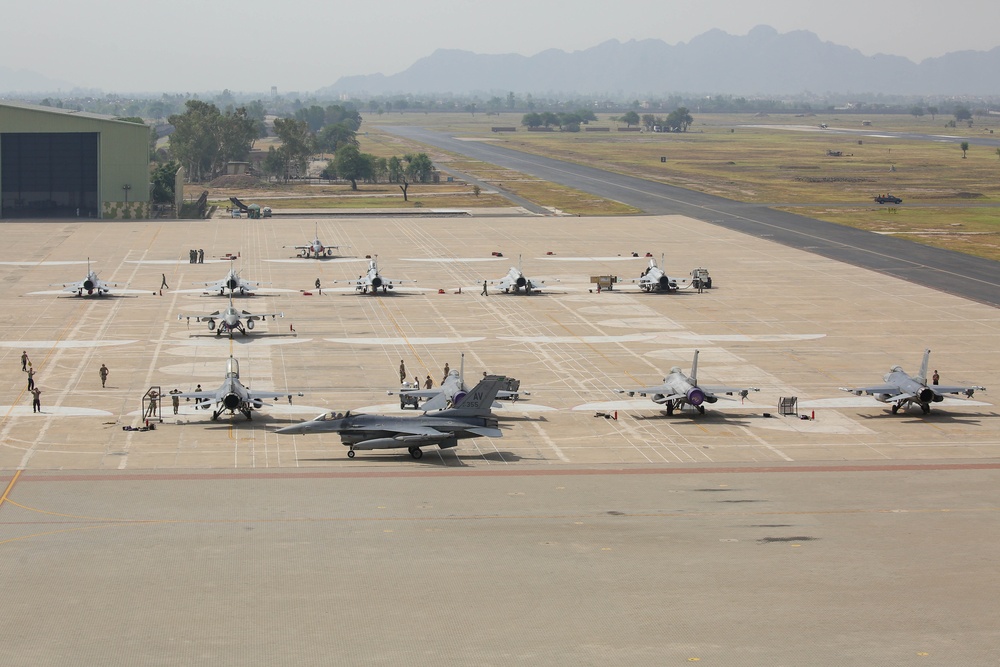
Currently, the IAF operates a 17-aircraft fleet of Ilyushin Il-76MDs, 105 Antonov An-32 aircraft, 12 Boeing C-17 Globemaster III, and 12 Lockheed Martin C-130J-30 Super Hercules. The older HS-748 aircraft are being replaced by the Airbus C-295MW.
The Indo-Russian Medium Transport Aircraft (MTA) project, initiated in 2009, aimed to replace the An-32 but has faced delays and technical issues, with Russia continuing the project alone. The Ilyushin Il-276, a potential outcome of this project, is expected to begin flight testing in 2023.
In December 2022, the IAF issued a Request for Information (RFI) for a new transport aircraft with an 18 to 30-ton capacity, extending the submission deadline to March 31, 2024. The RFI emphasizes technology transfer, indigenization, and establishing a manufacturing line in India.
The contenders for the contract are:
- Airbus A400M Atlas: A four-engine turboprop aircraft capable of carrying 37 tons and performing various roles, including medical evacuation and aerial refueling.
- Embraer C-390 Millennium: A twin-engine, jet-powered aircraft with a 26-ton payload, suitable for multiple missions and known for its operational flexibility and low costs.
- Lockheed Martin C-130J Super Hercules: A four-engine turboprop with a 19-ton payload, already in service with the IAF and known for its reliability and performance.
The evaluation process will consider technical specifications, life cycle costs, technology transfer levels, and potential for local manufacturing. The decision will also account for the aircraft's ability to operate from short, rough airstrips and support high-altitude operations.
India's defense acquisition processes are often lengthy, but the need for modernizing the IAF’s transport fleet is urgent to avoid capability gaps. Lockheed Martin, Airbus, and Embraer are all well-acquainted with India, with each offering distinct advantages and extensive collaboration history.
Lockheed Martin, in particular, is also pitching its F-21 fighter aircraft to the IAF, emphasizing its long-term presence in India and integration of Indian suppliers into its global supply chain. Airbus, with its significant civil aviation footprint in India, and Embraer, known for its advanced technologies and collaborations, are formidable competitors in this high-stakes battle for IAF contracts.