In response to increasing tensions with China, the Indian Air Force (IAF) is upgrading infrastructure at 20 eastern airbases, enhancing capabilities to handle China-centric operations. This includes constructing hardened aircraft shelters, munitions centers, and additional runways to accommodate increased civilian traffic and ensure operational continuity in case of runway damage during conflict.
A notable upgrade is the construction of a second runway at the strategic Leh airbase in Ladakh, a region of frequent India-China military clashes. Leh airbase is essential for maintaining operations along the Line of Actual Control with China and Siachen. The base supports night operations for fighters and transport aircraft, including Rafales, MiG-29s, Sukhoi-30s, and Apaches, and is vital for transporting troops and supplies during harsh winters when road access is limited.
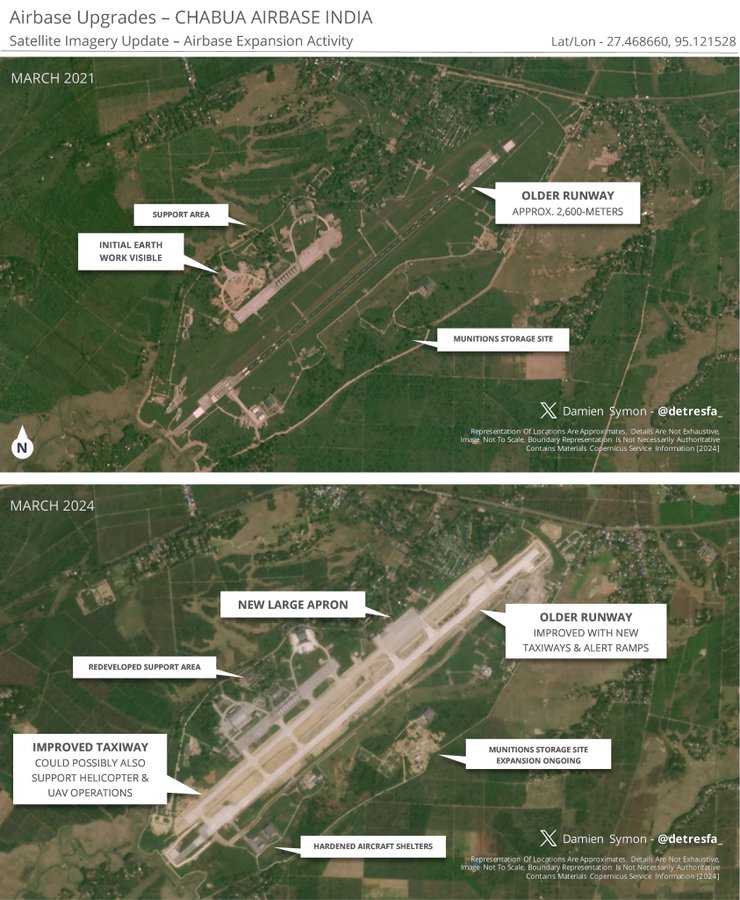
The IAF’s infrastructure development extends to other key bases. Satellite imagery from April 2024 revealed significant enhancements at the Chabua Air Base, near the China border. Upgrades include additional taxiways, hardened shelters for fighter aircraft, underground munitions storage, and improved taxiways for drones, ensuring sustained high-tempo operations if tensions escalate.
In Ladakh, a new 2.7-km runway at Nyoma airbase, located 23 kilometers from the China border, is set for completion in October 2024. The new runway, at an elevation of 13,700 feet, will enhance IAF operations. Support infrastructure, such as hangars, air traffic control buildings, and hard standing areas, will be ready by the end of 2025. Nyoma airstrip, operational during the 1962 India-China war, was reactivated in 2009 and has since supported various military aircraft, including the C-130J Super Hercules.
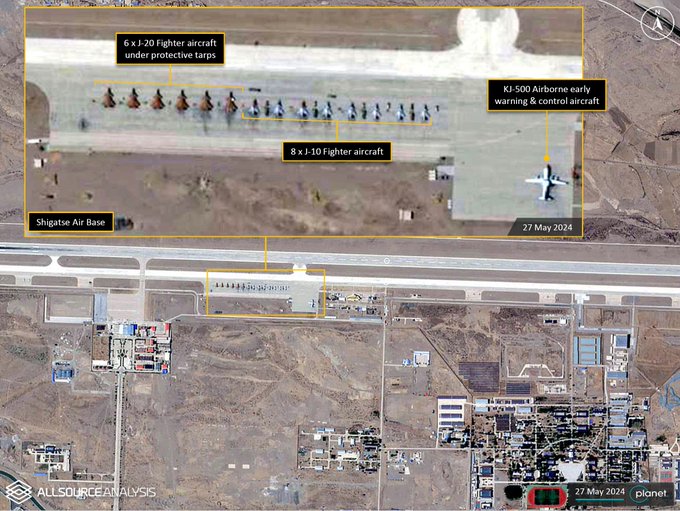
China has been ramping up its air assets along the LAC since the 2020 Galwan standoff. Recent satellite images show the deployment of China’s Chengdu J-20 Mighty Dragon 5th-generation fighter jets at Shigatse Air Base, only 150 kilometers from the LAC. The base also hosts J-10 aircraft and KJ-500 Airborne early warning and control aircraft, posing a strategic challenge to India's Rafale-equipped Hasimara Air Base in West Bengal.
The Shigatse base, with its new 3,000-meter auxiliary runway and multiple helipads, is strategically located along the central China-India border, close to the Doklam area, site of a 2017 standoff. The oblique angle of the new runway complicates enemy strikes aiming to disable both runways simultaneously.
China’s infrastructure expansion along the LAC since 2020, which includes new airbases, missile sites, roads, bridges, bunkers, and underground facilities, has significantly enhanced its military capabilities. The Hotan airbase in Xinjiang now features a new runway, additional tarmacs, hangars, and upgraded air defenses.
According to the China Power Project at the Centre for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), China has upgraded dozens of airports and heliports in Tibet and Xinjiang, improving last-mile connectivity and enabling a wider range of military operations. Open-source data identifies 37 newly constructed or upgraded air facilities in these regions since 2017, with at least 22 being military or dual-use. The accelerated development in 2020, including the construction and upgrading of 14 air facilities, fills previous gaps along the Indian border, providing the PLA Air Force (PLAAF) new bases to project airpower against India.